The power industry continues to be a hotbed of patent innovation. Activity is driven by wind turbine blade expansion to generate more power from onshore and offshore wind power plants, high strength, and low weight, and growing importance of technologies such as wind turbines, offshore wind, and onshore wind. In the last three years alone, there have been over 695,000 patents filed and granted in the power industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in power: fiber-reinforced turbine blades. Buy the report here.
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilizing and reaching maturity.
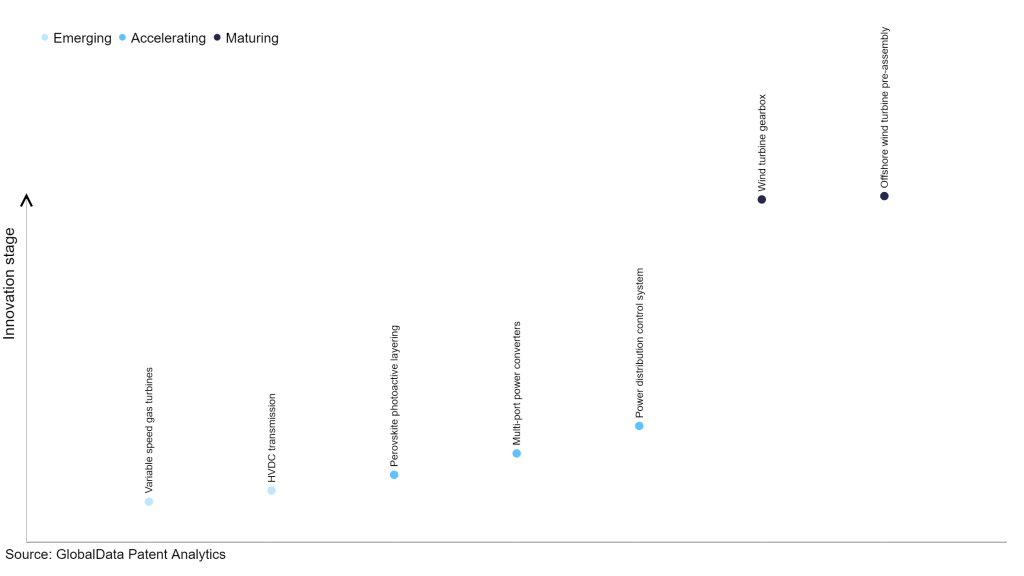
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
45+ innovations will shape the power industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the power industry using innovation intensity models built on over 83,000 patents, there are 45+ innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, variable speed gas turbines and HVDC transmission are the disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Perovskite photoactive layering, multi-port power converters, and power distribution control system are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are wind turbine gearbox and offshore wind turbine pre-assembly, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for the power industry
Fiber-reinforced composite turbine blades is a key innovation area in power
Wind turbine blades made of fiber-reinforced composites are frequently used in the production of large-scale wind turbines.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 35+ companies, spanning technology vendors, established power companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of fiber-reinforced composite turbine blades.
Key players in fiber-reinforced composite turbine blades – a disruptive innovation in the power industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of applications identified for each patent. It broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of countries each patent is registered in. It reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Patent volumes related to fiber-reinforced composite turbine blades
| Company | Total patents (2021 - 2023) | Premium intelligence on the world's largest companies |
| General Electric Co | 500 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Siemens AG | 263 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Vestas Wind Systems AS | 236 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Wobben Properties Gmbh | 79 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Senvion SA | 33 | Unlock Company Profile |
| TPI Composites Inc | 29 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Aloys Wobben Foundation | 21 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Nordex SE | 19 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Xiangtan Electric Manufacturing Co Ltd | 16 | Unlock Company Profile |
| CRRC Group Co., Ltd. | 16 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Arkema SA | 14 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Hexcel Corp | 13 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Gurit Holding AG | 13 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Neptco Inc | 13 | Unlock Company Profile |
| The Boeing Co | 12 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Covestro AG | 11 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Safran SA | 11 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd | 6 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Doosan Corp | 6 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft- und Raumfahrt eV | 5 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Schaeffler AG | 4 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Suzhou Red Maple Wind Blade Mould Co. Ltd. | 4 | Unlock Company Profile |
| BASF SE | 3 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Windfin BV | 3 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Envision Energy (Denmark) Aps | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Swancor Holding Co Ltd | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| LM Wind Power (R&D) Holland B.V | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Darwind Holding BV | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Envision Energy Ltd | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Hayden Paul | 2 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Carbon Rotec GmbH & Co. KG | 1 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Shanghai Electric Group Corp | 1 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Gamesa Innovation & Technology, S.L. | 1 | Unlock Company Profile |
| UT-Battelle, LLC | 1 | Unlock Company Profile |
| Gamesa SA | 1 | Unlock Company Profile |
Source: GlobalData Patent Analytics
Vestas Wind Systems is one of the leading patent filers in fiber-reinforced composite turbine blades. Vestas is a renewable energy company. It designs, manufactures, installs, and provides services to onshore and offshore power converters, wind turbines, blades, and towers. The company’s solutions encompass parts and repair to preventive inspections and advanced repairs. The service offerings of Vestas include data-driven consultancy, fleet optimization, blade maintenance and inspection, power generator repairs, and gearbox exchange. It partners with customers to monitor wind energy production and performance of the wind power plant throughout its lifetime. Some other key patent filers include General Electric, Siemens, and Wobben Properties.
In terms of application diversity, Lm Wind Power Us Technology leads the pack. LM Wind Power (R&D) and Wobben Properties stand in second and third positions, respectively.
By means of geographic reach, Gamesa, Vestas Wind Systems, BASF, and Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft- und Raumfahrt are some of the leading patent filers in fiber-reinforced composite turbine blades.
To further understand the key themes and technologies disrupting the power industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Power.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.



